|
Size: 1525
Comment:
|
Size: 11673
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
== Definitions == '''CompareOBJ RMS:''' The root mean square of the distance from each bigmap pixel/line location to the nearest facet of the truth OBJ.<<BR>> '''PTG:''' The formal camera pointing uncertainty.<<BR>> '''SCOBJ:''' The S/C position vector from the center of the asteroid.<<BR>> '''VSO:''' The formal SCOBJ uncertainty.<<BR>> == Additional Tests == === S/C position and pointing uncertainties === The Detailed Survey PolyCam F3G data set had large S/C position and pointing uncertainties, unsuitable for Detailed Survey Baseball Diamond trajectories: * VSO = 1km; * PTG = 1mrad. An additional suite of tests was therefore run with a duplicate Detailed Survey PolyCam dataset with S/C position and pointing uncertainties set to one-sigma: * VSO = 6.4m; * PTG = 0.217mrad. Results for both data sets are presented herein. === Model shift === In the process of generating the 35cm Preliminary Shape Model a shift in the body center with respect to the inertial center occurred. The magnitude of the shift was approximately 2m. Since the final S/C position across F3G subtests lay in a region 2m to 8m from the true S/C position, the effect of the body center shift came into question. To investigate, an alternative 35cm Preliminary Shape Model with no body-center shift was generated. One subtest was re-run using the alternative start model. == Key Findings == CompareOBJ RMSs (with and without translation/rotation) show no trend with the magnitude of S/C position and pointing perturbation within the perturbation ranges tested. The correlation score does not vary across subtests and is approx. 0.76 giving a very good indication of correlation. The accuracy of the evaluation model is therefore not dependent on the S/C position or camera pointing perturbation up to three standard deviations. The results show no significant difference in the final S/C position (SCOBJ) and model accuracy (as measured with CompareOBJ RMS) with respect to the magnitude of S/C position and pointing perturbation within the ranges tested, indicating that the SPC-driven modeling is immune to S/C position and pointing perturbation up to three standard deviations. It should be noted that S/C position perturbation was divided equally between the SCOBJ components, resulting in a distance from the truth position which was a multiple of the standard deviation of 6.4m. Therefore: * maximum lateral perturbation was a multiple of 3.7m (6.4m/sqrt(3)); * maximum normal perturbation (wrt body center) was 3.7m (6.4m/sqrt(3)). It is assumed that the worst case scenario is a 3 x sigma (19.2m) lateral perturbation. The maximum possible lateral perturbation tested was 3 x 3.7m = 11.1m. In all cases, the final SPC-derived S/C position is within 8m of the true S/C position, but in only two cases is within 2m of the true S/C position. The actual distance from the true S/C position is not dependent on the initial perturbed position - for example in the 0.25 x sigma case, the SPC-derived S/C position (distance from truth: 1.6m to 6.9m) in most cases moves further away from the true S/C position than its initial position (distance from truth: 1.6m). The final SPC-derived S/C positions appear to be clustered around an incorrect solution 2m-8m distant from the true S/C position. |
|
| Line 5: | Line 44: |
| {{attachment:CompareOBJ_RMS_resized.png}} | Three CompareOBJ RMS values are presented for each subtest and each S/C position and camera pointing uncertainty: * The largest CompareOBJ RMS (approx. 65cm across subtests) is obtained by running CompareOBJ on the untranslated and unrotated evaluation model. * The second smallest CompareOBJ RMS (approx. 15cm across subtests) is obtained by running CompareOBJ with its optimal translation and rotation option. * The smallest CompareOBJ RMS (approx. 9cm across subtests) is obtained by manually translating the evaluation model and searching for a local CompareOBJ RMS minimum. The CompareOBJ optimal translation routine is not optimized for the evaluation model scale (5cm pix/line resolution). Manual translations of the bigmap were therefore conducted in an attempt to find a minimum CompareOBJ RMS. The manually translated evaluation models gave the smallest CompareOBJ RMSs. The CompareOBJ RMS (for the final 5cm resolution 20m x 20m evaluation bigmap) does not appear to be affected by the magnitude of S/C position and pointing perturbation within the ranges tested. CompareOBJ RMSs differ slightly with S/C position and camera pointing uncertainties: * approx. 5cm difference for CompareOBJ RMS without translation/rotation; * approx. 2cm difference for CompareOBJ RMS with optimal translation and rotation; * approx. 0.4cm difference for CompareOBJ RMS with manual translation. {{attachment:CompareOBJ_VSO_1km_resized60pt.png}} {{attachment:CompareOBJ_VSO_1sigma_resized60pt.png}} '''CompareOBJ Optimal Translations:''' ||'''Sub-Test'''||'''S/C Position Uncertainty'''||'''Perturbation Magnitude'''||'''RMS (cm)'''||||||'''Translation (cm)'''||'''Translated Distance (cm)'''|| ||F3G7a||1km||0.25 x sigma||15.7849||85.0698||62.3596||-14.3765||106.4532|| ||F3G6a||1km||0.50 x sigma||15.1147||84.5538||61.6624||-15.3434||105.7687|| ||F3G5a||1km||0.75 x sigma||14.3150||95.8438||59.9313||-21.6901||115.1011|| ||F3G3a||1km||1.00 x sigma||13.6399||106.4870||58.2162||-27.3527||124.4057|| ||F3G4a||1km||1.50 x sigma||15.8949||79.1224||63.2865||-19.6432||103.2056|| ||F3G2a||1km||2.00 x sigma||13.6938||110.1339||58.9454||-23.2403||127.0596|| ||F3G1a||1km||3.00 x sigma||14.6271||93.5937||61.6997||-26.8422||115.2698|| ||'''Sub-Test'''||'''S/C Position Uncertainty'''||'''Perturbation Magnitude'''||'''RMS (cm)'''||||||'''Translation (cm)'''||'''Translated Distance (cm)'''|| ||F3G7b||6.4m||0.25 x sigma||15.9614||95.5555||66.8688||-17.6793||117.9613|| ||F3G6b||6.4m||0.50 x sigma||16.0260||93.7254||66.9687||-17.2331||116.4743|| ||F3G5b||6.4m||0.75 x sigma||16.4387||88.3626||69.0785||-12.1628||112.8172|| ||F3G3b||6.4m||1.00 x sigma||9.5449||167.5406||57.3951||-27.0780||179.1571|| ||F3G4b||6.4m||1.50 x sigma||16.0525||93.4737||70.0956||-15.0998||117.808=1|| ||F3G2b||6.4m||2.00 x sigma||16.1591||94.1139||69.1165||-19.95051||118.4514|| ||F3G1b||6.4m||3.00 x sigma||15.2938||101.8134||70.3467||-20.3179||125.4091|| '''CompareOBJ Manual Translations:''' ||'''Sub-Test'''||'''S/C Position Uncertainty'''||'''Perturbation Magnitude'''||'''RMS (cm)'''||||||'''Translation (cm)'''||'''Translated Distance (cm)'''|| ||F3G7a||1km||0.25 x sigma||8.0140||187.5||47.5||-30||195.74|| ||F3G6a||1km||0.50 x sigma||7.9343||187.5||47.5||-30||195.74|| ||F3G5a||1km||0.75 x sigma||7.9579||187.5||47.5||-30||195.74|| ||F3G3a||1km||1.00 x sigma||7.6749||187.5||47.5||-30||195.74|| ||F3G4a||1km||1.50 x sigma||7.9964||187.5||47.5||-40||197.52|| ||F3G2a||1km||2.00 x sigma||7.8591||187.5||47.5||-40||197.52|| ||F3G1a||1km||3.00 x sigma||7.6739||187.5||47.5||-50||209.19|| ||'''Sub-Test'''||'''S/C Position Uncertainty'''||'''Perturbation Magnitude'''||'''RMS (cm)'''||||||'''Translation (cm)'''||'''Translated Distance (cm)'''|| ||F3G7b||6.4m||0.25 x sigma||8.4097||207.5||47.5||-30||214.9709|| ||F3G6b||6.4m||0.50 x sigma||8.3974||207.5||47.5||-30||214.9709|| ||F3G5b||6.4m||0.75 x sigma||8.5008||207.5||47.5||-30||214.9709|| ||F3G3b||6.4m||1.00 x sigma||8.2400||207.5||47.5||-40||216.5929|| ||F3G4b||6.4m||1.50 x sigma||8.5820||197.5||57.5||-20||206.6700|| ||F3G2b||6.4m||2.00 x sigma||8.4134||197.5||57.5||-30||207.8762|| ||F3G1b||6.4m||3.00 x sigma||7.9259||197.5||57.5||-30||207.8762|| == Cross Correlation Scores == The evaluation maps were compared with a truth map via a cross-correlation routine which derives a correlation score. As a guide the following scores show perfect and excellent correlations: * A map cross-correlated with itself will give a correlation score of approx. 1.0; * Different sized maps sampled from the same truth (for example a 1,100 x 1,100 5cm sample map and a 1,000 x 1,000 5cm sample map) give a correlation score of approx. 0.8. The correlation scores show no trend with S/C position and camera pointing perturbation in the perturbation-range tested. The correlation scores also do not differ with S/C position and camera pointing uncertainties. The correlation score across subtests is approx. 0.76 giving a very good indication of correlation. '''Correlation Scores:''' ||'''Sub-Test'''||'''S/C Position Uncertainty'''||'''Perturbation Magnitude'''||'''Correlation Score'''|| ||F3G7a||1km||0.25 x sigma||0.7619|| ||F3G6a||1km||0.50 x sigma||0.7625|| ||F3G5a||1km||0.75 x sigma||0.7617|| ||F3G3a||1km||1.00 x sigma||0.7641|| ||F3G4a||1km||1.50 x sigma||0.7684|| ||F3G2a||1km||2.00 x sigma||0.7537|| ||F3G1a||1km||3.00 x sigma||0.7679|| ||'''Sub-Test'''||'''S/C Position Uncertainty'''||'''Perturbation Magnitude'''||'''Correlation Score'''|| ||F3G7b||6.4m||0.25 x sigma||0.7628|| ||F3G6b||6.4m||0.50 x sigma||0.7633|| ||F3G5b||6.4m||0.75 x sigma||0.7637|| ||F3G3b||6.4m||1.00 x sigma||0.7672|| ||F3G4b||6.4m||1.50 x sigma||0.7606|| ||F3G2b||6.4m||2.00 x sigma||0.7510|| ||F3G1b||6.4m||3.00 x sigma||0.7683|| |
| Line 9: | Line 133: |
| The first graph shows footprints for all Detailed Survey PolyCam images which were included in the model. The second graph shows the four images down-selected due to their coverage of the 20m x 20m evaluation region, and their almost complete containment within the iterated 100m x 100m region. | The first graph shows footprints for all Detailed Survey PolyCam pictures which were included in the model. The second graph shows the four pictures down-selected due to their coverage of the 20m x 20m evaluation region, and their almost complete containment within the iterated 100m x 100m region. |
| Line 17: | Line 141: |
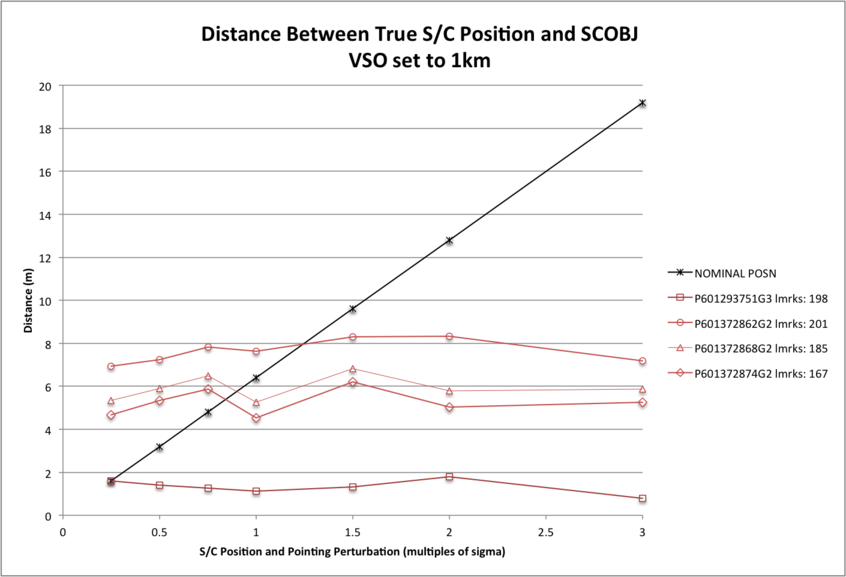
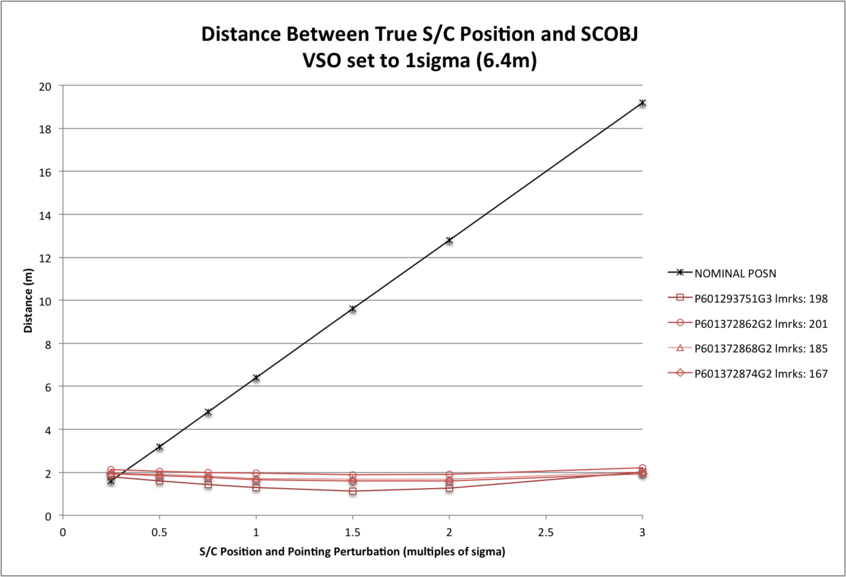
| Distance magnitude is plotted for the full Detailed Survey PolyCam image set. 3D graphs of final SCOBJ and truth is then plotted for each image. The first four are the down-selected evaluation images, the rest of the set is included for comparison. | The distance of the final SPC-derived S/C position from the true S/C position is plotted for the evaluation Detailed Survey PolyCam image set for each magnitude of perturbation. The distance of the final SCOBJ from the true S/C position is invariant with the perturbation to the initial SCOBJ within the perturbation-range tested. The variance in distances across pictures does vary with S/C position uncertainty however, with: * distances ranging from approx. 1m to 8m with VSO=1km; * distances ranging from approx. 1m to 2m with VSO=6.4m (1 sigma). |
| Line 19: | Line 145: |
| {{attachment:scobj_distance_resized.png}} | {{attachment:SCOBJ_distance_VSO_1km_resized60pct.png}} {{attachment:SCOBJ_distance_VSO_1sigma_resized60pct.png}} == SCOBJ == 3D graphs of final SPC-derived SCOBJ and true SCOBJ are then plotted for each picture. The first four are the down-selected evaluation pictures, the rest of the image set is included for comparison. The pattern of final SPC-derived SCOBJ is broadly consistent across magnitudes of perturbation. The position correction is mostly a normal correction with lateral movement, bringing the modeled S/C position within an approx. 8m-radius sphere around the true position (or, in the case of perturbations<8m, pushing SCOBJ outwards up to 8m). |
| Line 23: | Line 157: |
| '''Example nominal SCOBJs:''' |
|
| Line 24: | Line 160: |
''' Final solution SCOBJs:''' {{attachment:P601293751G3_final_resized.png}} |
|
| Line 34: | Line 174: |
{{attachment:P601293751G3_final_resized.png}} |
TestF3G - Results
Definitions
CompareOBJ RMS: The root mean square of the distance from each bigmap pixel/line location to the nearest facet of the truth OBJ.
PTG: The formal camera pointing uncertainty.
SCOBJ: The S/C position vector from the center of the asteroid.
VSO: The formal SCOBJ uncertainty.
Additional Tests
S/C position and pointing uncertainties
The Detailed Survey PolyCam F3G data set had large S/C position and pointing uncertainties, unsuitable for Detailed Survey Baseball Diamond trajectories:
- VSO = 1km;
- PTG = 1mrad.
An additional suite of tests was therefore run with a duplicate Detailed Survey PolyCam dataset with S/C position and pointing uncertainties set to one-sigma:
- VSO = 6.4m;
- PTG = 0.217mrad.
Results for both data sets are presented herein.
Model shift
In the process of generating the 35cm Preliminary Shape Model a shift in the body center with respect to the inertial center occurred. The magnitude of the shift was approximately 2m. Since the final S/C position across F3G subtests lay in a region 2m to 8m from the true S/C position, the effect of the body center shift came into question. To investigate, an alternative 35cm Preliminary Shape Model with no body-center shift was generated. One subtest was re-run using the alternative start model.
Key Findings
CompareOBJ RMSs (with and without translation/rotation) show no trend with the magnitude of S/C position and pointing perturbation within the perturbation ranges tested. The correlation score does not vary across subtests and is approx. 0.76 giving a very good indication of correlation. The accuracy of the evaluation model is therefore not dependent on the S/C position or camera pointing perturbation up to three standard deviations.
The results show no significant difference in the final S/C position (SCOBJ) and model accuracy (as measured with CompareOBJ RMS) with respect to the magnitude of S/C position and pointing perturbation within the ranges tested, indicating that the SPC-driven modeling is immune to S/C position and pointing perturbation up to three standard deviations.
It should be noted that S/C position perturbation was divided equally between the SCOBJ components, resulting in a distance from the truth position which was a multiple of the standard deviation of 6.4m. Therefore:
- maximum lateral perturbation was a multiple of 3.7m (6.4m/sqrt(3));
- maximum normal perturbation (wrt body center) was 3.7m (6.4m/sqrt(3)).
It is assumed that the worst case scenario is a 3 x sigma (19.2m) lateral perturbation. The maximum possible lateral perturbation tested was 3 x 3.7m = 11.1m.
In all cases, the final SPC-derived S/C position is within 8m of the true S/C position, but in only two cases is within 2m of the true S/C position. The actual distance from the true S/C position is not dependent on the initial perturbed position - for example in the 0.25 x sigma case, the SPC-derived S/C position (distance from truth: 1.6m to 6.9m) in most cases moves further away from the true S/C position than its initial position (distance from truth: 1.6m).
The final SPC-derived S/C positions appear to be clustered around an incorrect solution 2m-8m distant from the true S/C position.
CompareOBJ RMS
Three CompareOBJ RMS values are presented for each subtest and each S/C position and camera pointing uncertainty:
- The largest CompareOBJ RMS (approx. 65cm across subtests) is obtained by running CompareOBJ on the untranslated and unrotated evaluation model.
- The second smallest CompareOBJ RMS (approx. 15cm across subtests) is obtained by running CompareOBJ with its optimal translation and rotation option.
- The smallest CompareOBJ RMS (approx. 9cm across subtests) is obtained by manually translating the evaluation model and searching for a local CompareOBJ RMS minimum.
The CompareOBJ optimal translation routine is not optimized for the evaluation model scale (5cm pix/line resolution). Manual translations of the bigmap were therefore conducted in an attempt to find a minimum CompareOBJ RMS. The manually translated evaluation models gave the smallest CompareOBJ RMSs.
The CompareOBJ RMS (for the final 5cm resolution 20m x 20m evaluation bigmap) does not appear to be affected by the magnitude of S/C position and pointing perturbation within the ranges tested.
CompareOBJ RMSs differ slightly with S/C position and camera pointing uncertainties:
- approx. 5cm difference for CompareOBJ RMS without translation/rotation;
- approx. 2cm difference for CompareOBJ RMS with optimal translation and rotation;
- approx. 0.4cm difference for CompareOBJ RMS with manual translation.
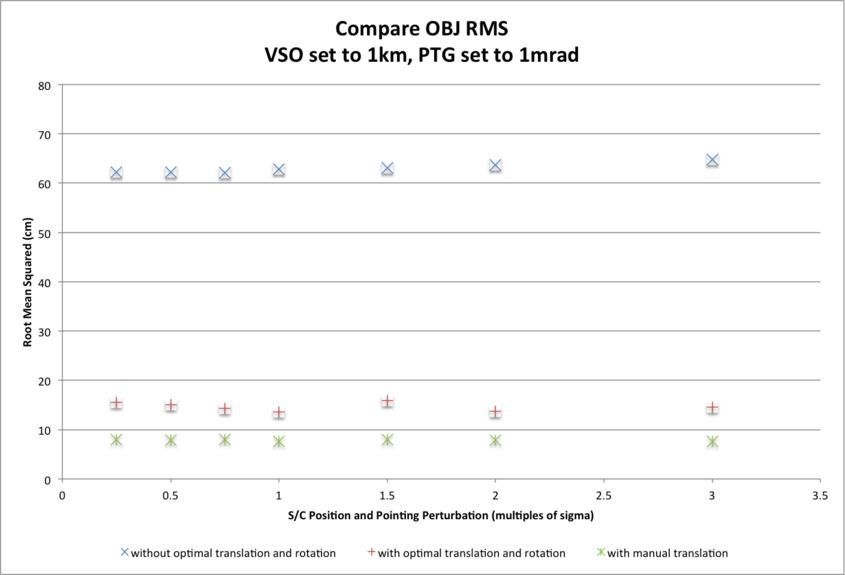
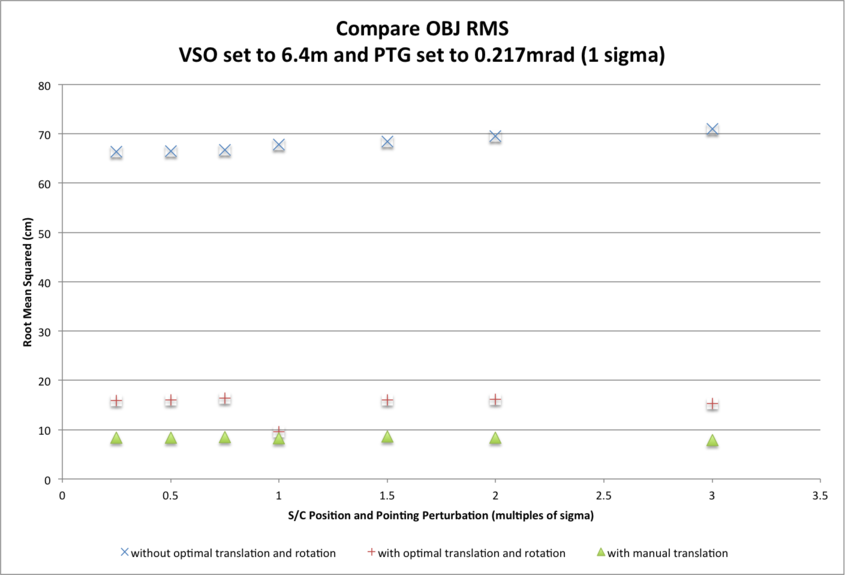
CompareOBJ Optimal Translations:
Sub-Test |
S/C Position Uncertainty |
Perturbation Magnitude |
RMS (cm) |
Translation (cm) |
Translated Distance (cm) |
||
1km |
0.25 x sigma |
15.7849 |
85.0698 |
62.3596 |
-14.3765 |
106.4532 |
|
1km |
0.50 x sigma |
15.1147 |
84.5538 |
61.6624 |
-15.3434 |
105.7687 |
|
1km |
0.75 x sigma |
14.3150 |
95.8438 |
59.9313 |
-21.6901 |
115.1011 |
|
1km |
1.00 x sigma |
13.6399 |
106.4870 |
58.2162 |
-27.3527 |
124.4057 |
|
1km |
1.50 x sigma |
15.8949 |
79.1224 |
63.2865 |
-19.6432 |
103.2056 |
|
1km |
2.00 x sigma |
13.6938 |
110.1339 |
58.9454 |
-23.2403 |
127.0596 |
|
1km |
3.00 x sigma |
14.6271 |
93.5937 |
61.6997 |
-26.8422 |
115.2698 |
|
Sub-Test |
S/C Position Uncertainty |
Perturbation Magnitude |
RMS (cm) |
Translation (cm) |
Translated Distance (cm) |
||
6.4m |
0.25 x sigma |
15.9614 |
95.5555 |
66.8688 |
-17.6793 |
117.9613 |
|
6.4m |
0.50 x sigma |
16.0260 |
93.7254 |
66.9687 |
-17.2331 |
116.4743 |
|
6.4m |
0.75 x sigma |
16.4387 |
88.3626 |
69.0785 |
-12.1628 |
112.8172 |
|
6.4m |
1.00 x sigma |
9.5449 |
167.5406 |
57.3951 |
-27.0780 |
179.1571 |
|
6.4m |
1.50 x sigma |
16.0525 |
93.4737 |
70.0956 |
-15.0998 |
117.808=1 |
|
6.4m |
2.00 x sigma |
16.1591 |
94.1139 |
69.1165 |
-19.95051 |
118.4514 |
|
6.4m |
3.00 x sigma |
15.2938 |
101.8134 |
70.3467 |
-20.3179 |
125.4091 |
|
CompareOBJ Manual Translations:
Sub-Test |
S/C Position Uncertainty |
Perturbation Magnitude |
RMS (cm) |
Translation (cm) |
Translated Distance (cm) |
||
1km |
0.25 x sigma |
8.0140 |
187.5 |
47.5 |
-30 |
195.74 |
|
1km |
0.50 x sigma |
7.9343 |
187.5 |
47.5 |
-30 |
195.74 |
|
1km |
0.75 x sigma |
7.9579 |
187.5 |
47.5 |
-30 |
195.74 |
|
1km |
1.00 x sigma |
7.6749 |
187.5 |
47.5 |
-30 |
195.74 |
|
1km |
1.50 x sigma |
7.9964 |
187.5 |
47.5 |
-40 |
197.52 |
|
1km |
2.00 x sigma |
7.8591 |
187.5 |
47.5 |
-40 |
197.52 |
|
1km |
3.00 x sigma |
7.6739 |
187.5 |
47.5 |
-50 |
209.19 |
|
Sub-Test |
S/C Position Uncertainty |
Perturbation Magnitude |
RMS (cm) |
Translation (cm) |
Translated Distance (cm) |
||
6.4m |
0.25 x sigma |
8.4097 |
207.5 |
47.5 |
-30 |
214.9709 |
|
6.4m |
0.50 x sigma |
8.3974 |
207.5 |
47.5 |
-30 |
214.9709 |
|
6.4m |
0.75 x sigma |
8.5008 |
207.5 |
47.5 |
-30 |
214.9709 |
|
6.4m |
1.00 x sigma |
8.2400 |
207.5 |
47.5 |
-40 |
216.5929 |
|
6.4m |
1.50 x sigma |
8.5820 |
197.5 |
57.5 |
-20 |
206.6700 |
|
6.4m |
2.00 x sigma |
8.4134 |
197.5 |
57.5 |
-30 |
207.8762 |
|
6.4m |
3.00 x sigma |
7.9259 |
197.5 |
57.5 |
-30 |
207.8762 |
|
Cross Correlation Scores
The evaluation maps were compared with a truth map via a cross-correlation routine which derives a correlation score. As a guide the following scores show perfect and excellent correlations:
- A map cross-correlated with itself will give a correlation score of approx. 1.0;
- Different sized maps sampled from the same truth (for example a 1,100 x 1,100 5cm sample map and a 1,000 x 1,000 5cm sample map) give a correlation score of approx. 0.8.
The correlation scores show no trend with S/C position and camera pointing perturbation in the perturbation-range tested. The correlation scores also do not differ with S/C position and camera pointing uncertainties. The correlation score across subtests is approx. 0.76 giving a very good indication of correlation.
Correlation Scores:
Sub-Test |
S/C Position Uncertainty |
Perturbation Magnitude |
Correlation Score |
1km |
0.25 x sigma |
0.7619 |
|
1km |
0.50 x sigma |
0.7625 |
|
1km |
0.75 x sigma |
0.7617 |
|
1km |
1.00 x sigma |
0.7641 |
|
1km |
1.50 x sigma |
0.7684 |
|
1km |
2.00 x sigma |
0.7537 |
|
1km |
3.00 x sigma |
0.7679 |
Sub-Test |
S/C Position Uncertainty |
Perturbation Magnitude |
Correlation Score |
6.4m |
0.25 x sigma |
0.7628 |
|
6.4m |
0.50 x sigma |
0.7633 |
|
6.4m |
0.75 x sigma |
0.7637 |
|
6.4m |
1.00 x sigma |
0.7672 |
|
6.4m |
1.50 x sigma |
0.7606 |
|
6.4m |
2.00 x sigma |
0.7510 |
|
6.4m |
3.00 x sigma |
0.7683 |
Image Footprints
The first graph shows footprints for all Detailed Survey PolyCam pictures which were included in the model. The second graph shows the four pictures down-selected due to their coverage of the 20m x 20m evaluation region, and their almost complete containment within the iterated 100m x 100m region.
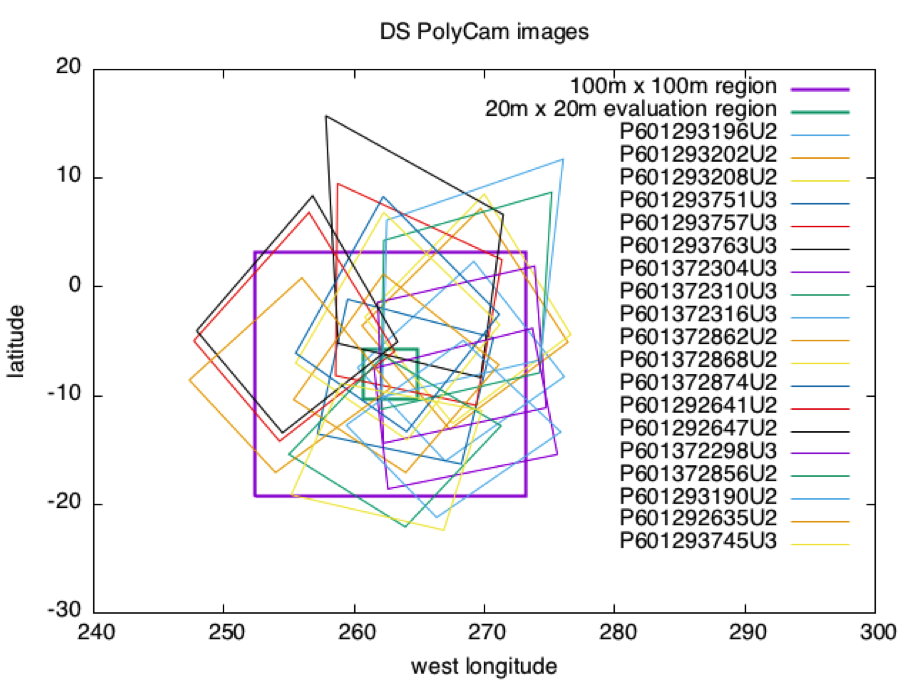
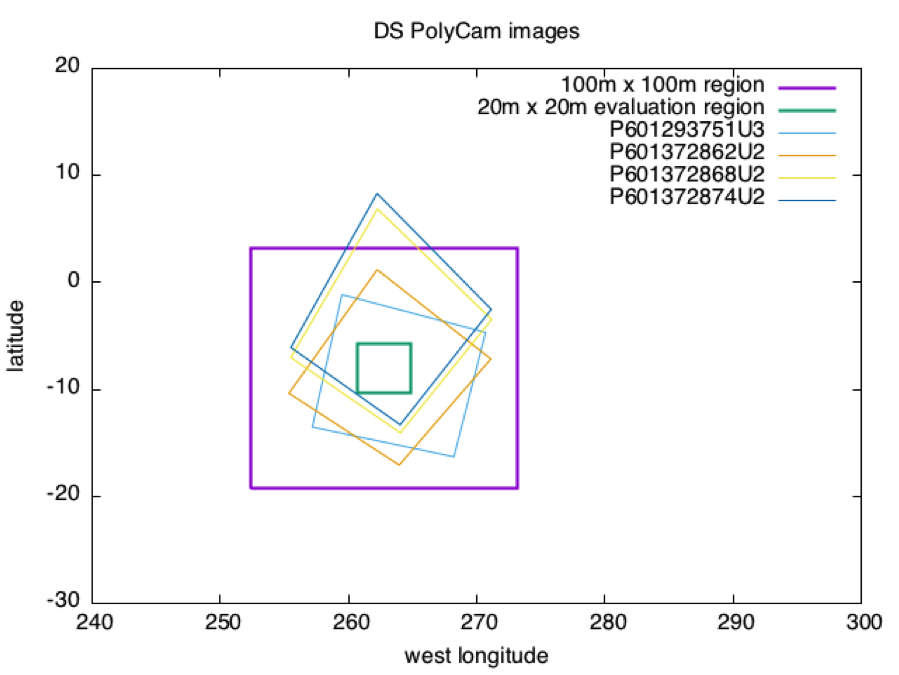
Distance SCOBJ(truth) to SCOBJ(solution)
The distance of the final SPC-derived S/C position from the true S/C position is plotted for the evaluation Detailed Survey PolyCam image set for each magnitude of perturbation. The distance of the final SCOBJ from the true S/C position is invariant with the perturbation to the initial SCOBJ within the perturbation-range tested. The variance in distances across pictures does vary with S/C position uncertainty however, with:
- distances ranging from approx. 1m to 8m with VSO=1km;
- distances ranging from approx. 1m to 2m with VSO=6.4m (1 sigma).
SCOBJ
3D graphs of final SPC-derived SCOBJ and true SCOBJ are then plotted for each picture. The first four are the down-selected evaluation pictures, the rest of the image set is included for comparison.
The pattern of final SPC-derived SCOBJ is broadly consistent across magnitudes of perturbation. The position correction is mostly a normal correction with lateral movement, bringing the modeled S/C position within an approx. 8m-radius sphere around the true position (or, in the case of perturbations<8m, pushing SCOBJ outwards up to 8m).
Evaluation Pictures
Example nominal SCOBJs:
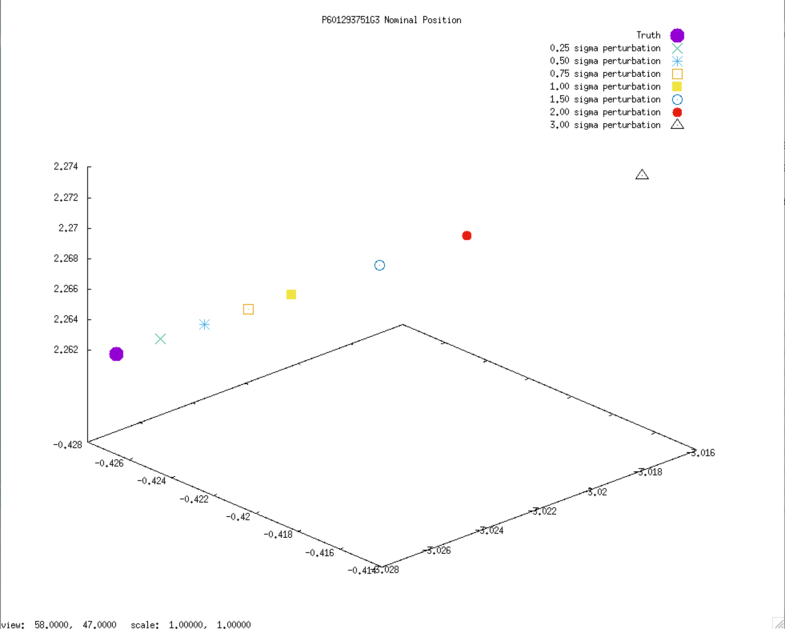
Final solution SCOBJs:
