residuals.e
Residuals tests the landmarks to look for problems. It will give you a report based on landmarks, pictures and maps.
Input - files
Input - stdin
- enter plim (px,km,km)
The number of pixels an images needs to be "off" to throw the chevron (>>) flag
- The rms error of a landmark
- Sets the "bin" size for the final histogram (basically how many images are in which side categories). input operation list
2.5, 1, 001
Output
Description
- Compares predicted and observed pixel, line position of the landmarks in the images
- Produces RSS of the diagonal convariance elements of each control point
- Describes landmark position uncertainty
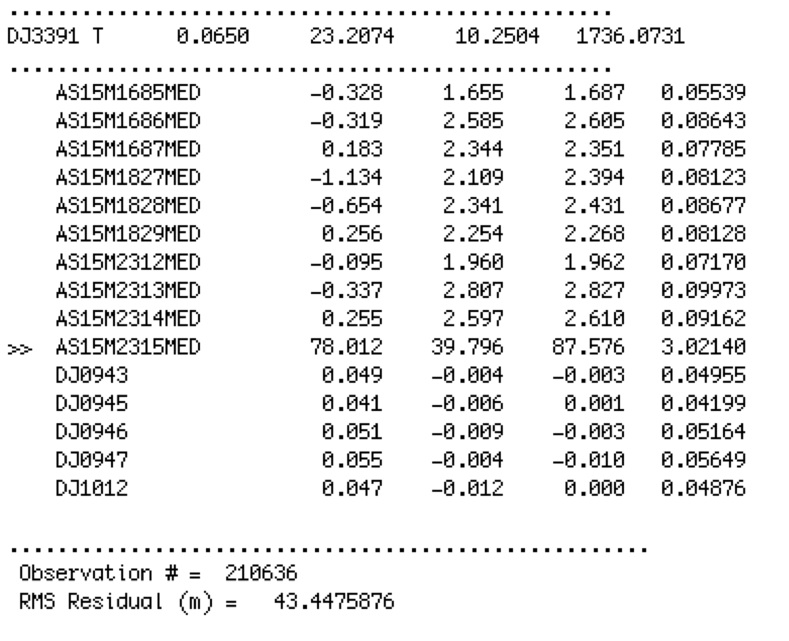
- Flags landmarks with residuals over specified pixel value
Control Points
- Inputs are wweights for S/C uncertainties from measurement uncertainties and from a-prior shape constraints
Control points solution results in a 3x3 output covariance for each control point. Diagonal elements are uncertainties along maplet coord. system axes, i.e. two horizontal directions & height. Typically SPC produces comparable horizontal & height uncertainties. Results are summarized as a scalar standard deviation per degree of freedom in meters
- Residuals check automatically flags errors beyond certain input values in dump file for ease of inspection
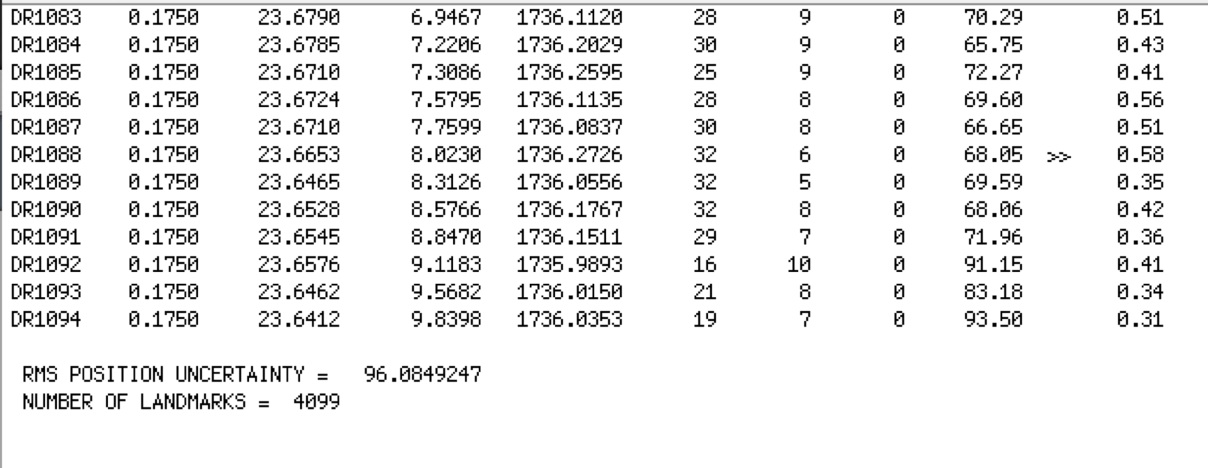
Image Residuals
- The post-fit residuals between predicted and actual control point positions in all images are captured in the residuals file
- The post-fit residuals between predicted and actual control point difference between adjacent, overlapping maplets are captured in the residuals file
- Outliers in both quantities are flagged automatically based on input threshold criteria
Qualitative Checks
- Qualitative checks are important to verify that the quantitative error estimates are believable
Render a single maplet, or a DEM synthesized by a collection of maplets, at the same geometry & illumination conditions as the images themselves
- Do all the features in the images appear in the DEM ?
- Are the smallest discernible features in the images, e.g., boulders, craters etc. visible in the DEM as well ?
- Is the relative albedo solution such that the relative brightness of adjacent image features matches that of the DEM ?
- Are the heights solution such that the length and overall appearance of the shadows in the DEM matches that of the image ?
How are Uncertainties Introduced in the Data
- Main types of uncertainties:
- S/C trajectory, camera pointing, image timestamp
- Manifest themselves mostly in the projection of image template onto the surface. Corrected by global geometry solution
- Image noise, artifacts, smear, overall image quality
- Manifest themselves in predicted image template brightness and in its fit to the extracted image brightness
- Photometric model and reflectance function models
Show up in slopes & heights integration
Poor choice of a-priori parameters & data weights
- Evident at end of each estimation step; data won’t fit well
- S/C trajectory, camera pointing, image timestamp
- Often above contributions are correlated; individual contributors may not be separated until many processing steps have been taken
